

The DISCO Knowledge Hub is an open-source digital platform designed to serve as a collaborative online space for stakeholders in the field of urban logistics and sustainable mobility. It offers a range of resources, tools, and opportunities for knowledge sharing, capacity building, innovation, and collaboration within this domain.
The DISCO Knowledge Hub aims to be the go-to place for stakeholders, to empower them with the tools, information, and connections needed to drive positive change and innovation in urban logistics and mobility.
The vision is to build a dynamic and comprehensive online collaboration platform that serves as a central focal point for urban logistics and sustainable mobility stakeholders.
Visit DISCO's website for more!
Discover Living Labs Insights for a concise overview of innovative solutions, projects, and technical deliverables. Stay updated with regular insights featuring descriptive articles and visuals directly from the Living Labs. Explore ongoing advancements and progress within our Living Labs projects.
Explore DISCO Living Lab Innovations for in-depth insights into groundbreaking projects and solutions. Delve into a comprehensive overview of ongoing initiatives within our Living Labs, highlighting their impactful contributions to innovation and problem-solving. Get updates and insights directly from our DISCO Living Labs, exploring the latest developments, progress reports, and innovative solutions as we share regular updates on ongoing initiatives and projects within our Living Labs network.
 |
The City of Copenhagen is one of the selected EU Mission 100 climate-neutral and smart cities by 2030. To reach its climate objectives and deploy zero-emission logistic solutions, Copenhagen is taking an integrated approach through DISCO to ensure that the entire functional urban area benefits from the transition. The City recognises that its policies will affect local stakeholders, and will therefore work closely with industry sectors, citizens, and public authorities to ensure desirable outcomes for all. |
 |
The City of Ghent is a medium-sized medieval European city surrounded by an inner ring and outer ring (R4). In the historic centre, Ghent has a pedestrian area of 2 km². The municipality has incorporated many efforts to green the city including a modal shift as a cornerstone in Ghent’s SUMP 2014 and in 2019, a low-emission zone and a “Vision for the Use of Water in the City” which focuses on developing the use of waterways for freight transport. Ghent also aims to be climate neutral by 2050. |
|---|
 |
The City of Thessaloniki is one of the 100 EU Mission climate-neutral and smart cities by 2030. The City’s challenge is to become a zero-emission city by 2030, achieve optimised use of public space and overall enhanced citizens’ quality of life. Currently, in the historical centre, the main demand generators for last-mile transport are the commercial establishments and, more specifically, from fashion and HORECA. |
|---|
The City of Helsinki is one of the 100 EU Mission 2030 climate-neutral and smart cities. Helsinki logistics operations are currently primarily led by private companies, but the city has an ambition to support the logistics field towards a new sustainable operational model in line with the action plan for city logistics, updated in 2020. In Helsinki, delivery trucks 22-26% of traffic emissions in the city. The overall share of vans used for last-mile logistics is unknown, but most vans are used for other purposes. |
|---|
The Zaragoza Living Lab will enhance its last mile delivery thanks to an adapted Control Tower of multi stakeholder delivery management. It will boost local commerce via the integration and enhancement of the Citizen Card and the Volveremos groupon program, which provide an understanding of the transport and social behaviours. The Data Space will be utilised as a solid platform to create added value to the city by developing a vision and a work line withinthe City’s #DataLab team’s adapted to the guidelines of the Data Act initiative. |
|---|
 |
The Valencia Living Lab will implement a Supply Chain Hub (SCH), a flexible logistics facility in which several supply chains that serve the B2B/B2C last mile will be managed. In DISCO, AI will be used for the consolidation and regrouping of loads (multisector and multiproduct), unification of the distribution in a single fleet of zero-emission vehicles (100% electric designed to carry out an operationally efficient last mile distribution). |
|---|
 |
Barcelona, Valencia, and Zaragoza have established a well-connected cluster of cities belonging to the same country (Spain) to empower the positive effects of implementation, uptake, and replication potentials of sets of complementary measures on a larger scale and in various local conditions. All the three cities have ambitious plans and sustainable goals and have therefore all been selected as part of the “100 EU Mission climate-neutral and smart cities by 2030”. |
|---|
The City of Padua is a major centre for services, tourism, and culture, and is surrounded by a large, dynamic area that has experienced significant growth in recent years and, as such, is a significant generator of travel.The city is well connected with neighbouring cities in the Veneto Region, and with long-distance transport networks. It is one of the selected 100 EU “Mission climate-neutral and smart cities by 2030” |
|---|
 |
DISCO stands for ‘Data-driven, Integrated, Syncromodal, Collaborative and Optimised urban freight meta-model for a new generation of urban logistics and planning with data sharing at European Living Labs’. Our aim is simple: to support the EU mission cities in achieving their climate goals by 2030, letting our living spaces breathe new life away from air pollutants.How? We will drive EU Cities towards a Physical Internet (PI) approach that aims to overcome possible trade-offs between the accessibility of goods and services, quality of life and environmental aspects necessitating fewer kms travelled to deliver the same amount of goods. |
|---|
 |
|
|---|
 |
Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
|
|---|
 |
The Urban Freight Data Space (UFDS) aims to revolutionise urban logistics by enabling data sharing and collaboration among stakeholders. This project focuses on developing a secure and standardized data-sharing platform that supports data sovereignty. By integrating diverse data sources, UFDS will empower stakeholders to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and contribute to more sustainable urban logistics solutions. This DISCO deliverable outlines the architecture and development plan for UFDS, highlighting its potential to transform the industry.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
|
|---|
 |
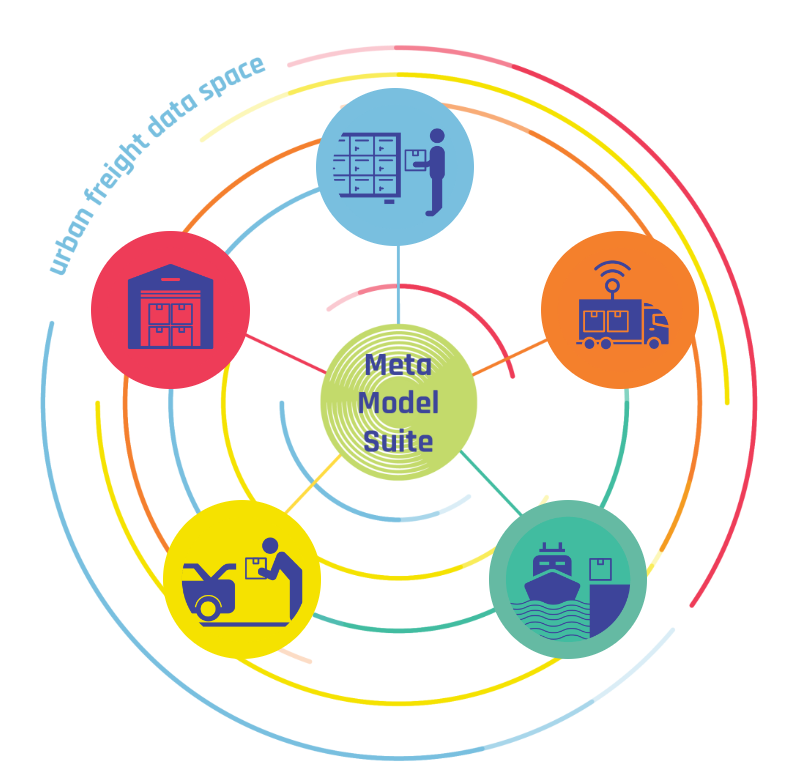
The DISCO Meta Model Suite (MMS) is a key component of the DISCO project aimed at improving urban logistics. It is designed to address the challenges posed by increasing urbanization, e-commerce, and environmental concerns. The MMS promotes collaboration, interoperability, and resource sharing, aligning with the principles of the Physical Internet. By leveraging advanced technologies and data-driven strategies, the MMS aims to create more efficient, sustainable, and responsive urban logistics systems.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
This Data Management Plan is the second version of the document and describes the data management processes for data generated within the DISCO project, including the methodologies and standards to be followed to ensure protection, security, and confidentiality. It details the updated list of datasets generated and guidelines for data management, aligning with FAIR principles. The plan intends to publish non-confidential results under Open Access and will be updated twice more during the project.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
This Data Management Plan is the second version of the document and describes the data management processes for data generated within the DISCO project, including the methodologies and standards to be followed to ensure protection, security, and confidentiality. It details the updated list of datasets generated and guidelines for data management, aligning with FAIR principles. The plan intends to publish non-confidential results under Open Access and will be updated twice more during the project.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
This article contribution to "Domus" magazine highlights the DISCO project as an innovative initiative advancing urban logistics through digitalization, hyperconnectivity, and collaboration. It emphasizes the concept of data spaces—secure environments for sharing logistical data—and the Physical Internet paradigm to improve the efficiency and sustainability of freight transport. The article also discusses pilot implementations in DISCO's eight cities, demonstrating shared infrastructure, digital twins, and sustainable last-mile delivery. By integrating advanced tools and fostering public-private collaboration, DISCO aims to guide cities toward zero-emission urban systems and smarter logistics management, offering practical solutions for planners and stakeholders.Link to the Magazine |
|---|
 |
During the DISCO Project meeting held in Cologne in October 2024, Anne Goodchild presented the findings from the Urban Freight Lab's DISCOCURB initiative. This project aimed to analyze commercial vehicle parking behaviors and the effectiveness of a new parking application, Open Park. The study involved a randomized experiment comparing delivery performance metrics between drivers using the app and those without it. Key results indicated that current curbspace management practices in Seattle are underutilized, with a significant percentage of commercial vehicles parking without permits. The presentation highlighted the need for improved enforcement and technology adoption to enhance curb management efficiency and compliance among commercial vehicle operators. Overall, the insights from ICBT experts emphasized the importance of data-driven approaches in urban freight logistics to foster better outcomes for both city infrastructure and service providers.Link to the Pdf |
|---|
 |
This presentation, delivered by Marianne Ryghaug from SINTEF, was part of the DISCO Project meeting held in Cologne in October 2024, focusing on " mission-oriented experiments " in urban logistics transformation as part of the EU Horizon Mission for Climate-Neutral and Smart Cities by 2030. Marianne Ryghaug emphasized the critical role of epistemic inclusion, which involves integrating technical, social, and local knowledge through open dialogues that address controversies and failures. The presentation outlined ten key recommendations aimed at fostering effective climate innovation, including normalizing the sharing of failures, recognizing non-linear innovation processes, and promoting citizen participation beyond mere acceptance to enable co-creation. Ryghaug highlighted that epistemic inclusion is essential for adapting governance structures and ensuring diverse knowledge integration, ultimately enhancing the efficacy of urban climate initiatives. The conclusion underscored that addressing climate change requires inclusive approaches and adaptive governance mechanisms to navigate complex societal challenges effectively.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
This presentation, delivered by Andreas Nettsträter, was part of the DISCO Project meeting held in Cologne in October 2024, focusing on the exchange of insights from ICBT experts. It emphasized the significance of open source in the logistics industry, highlighting how collaborative development can foster innovation in basic and commodity services that are typically non-market-differentiating. The Open Logistics Foundation serves as a neutral platform for creating open source solutions, enabling efficient data exchange and improving logistics processes such as digital air cargo and customs operations. The initiative aims to engage a diverse community of stakeholders, including logistics service providers and IT solution companies, to collectively enhance the industry's capabilities while ensuring that all contributions remain accessible and free of commercial interests.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
This presentation, delivered by Thomas Osdoba from NetZeroCities during the ICBT experts exchange in Cologne (October 2024), explored the role of Living Labs in catalyzing climate neutrality within the European Cities Mission.. Thomas Osdoba highlighted NetZeroCities’ comprehensive support, including the Climate Transition Map, NZC portal, pilot programs, and twinning initiatives. The session emphasized systemic innovation, aligning governance, policy, and business strategies, and fostering partnerships among cities, businesses, and communities. By innovating at local levels, replicable solutions were showcased, alongside insights into overcoming systemic barriers, scaling impact, and leveraging 20 years of shared practices to achieve sustainable urban transformation..Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
The document describes a Microhub concept designed to make urban logistics more sustainable and economically viable. Microhubs are small logistics centers located close to delivery areas, facilitating last-mile distribution by consolidating shipments and using lighter vehicles like cargo bikes and delivery robots. The concept aims to reduce emissions, air pollution, and congestion, while also improving business efficiency. Key aspects include a market-based business model, strategic location of hubs, efficient handling of small to medium-sized non-time-critical shipments, and the integration of services like parcel lockers.Link to the pdf |
|---|
|
|
DISCOLLECT has developed a Smart Data Platform (SDP) based on the Dagster database software to help cities onboard their data to the UFDS. The SDP consists of a data space connector, a database, and additional components for data scraping and conversion. Cities can use this framework to offer their data to the data space by connecting their open data portals to the SDP. As an example, Ghent has used this framework to offer parking data to the UFDS. The SDP scrapes parking data from Ghent's open data portal, converts it to the right standard, and connects it to the UFDS. Inlecom has then developed a 2D visualiser app that visualizes the parking data by pulling it from the SDP through a UFDS connector and a middleware component.
|
|---|
|
|
Whether data is required or data is to be shared with others: Users of a data space must be competent and understand the business, organizational and basic technical aspects of data spaces. The Data Space User Group is designed for professionals who want to understand, explore, and benefit from data spaces – without needing deep technical expertise.The User Group offers: engagement – regular opportunities to engage with peers, learn about solutions, and share data space needs –; business insight – all relevant data news and information –; and holistic knowledge and solutions arena – the most complete library of papers, guides, tools, and event recordings on data spaces as well as comprehensive access to all crucial data space solutions and services.Click here to get more information or to even start the certification process. |
|---|
 |
The foundation of data spaces is trust, which is established through a rigorous, transparent certification process. The most important component of a data space is the Data Space Connector. To make sure that each connector behaves as it should, it is certified against specific security standards and so is any data space participant. On this basis of trust the participants can start their actual sharing of data.For this International Data Spaces (IDS) Certification of data space components – and even of data space participants –, a certification scheme is applied that defines the rules, and standards of the certification process. The IDS certification scheme follows best practices from internationally accredited certification concepts.Click here to get more information or to even start the certification process. |
|---|
| |
Data spaces offer cities an excellent way to connect with logistics players and integrate valuable city data directly into logistics operations. However, making city data available on a data space can come with some challenges. From valuable logistics data being hidden in internal databases or unpublished archives, to the need for data conversion to international standards, these obstacles can make data sharing difficult. The Smart Data Platform provides a solution, offering a set of tools that help data engineers overcome these hurdles and connect city data sets to the data space.In the Meta Model Suite, users are guided through the entire process of deploying the platform, from importing and transforming unstructured data to automating data collection and publishing it to the data space. With the Smart Data Platform and embedded Data Space Connector, data isn't just exchanged—it's enriched, standardized, and shared as a valuable asset that can drive smarter business applications. |
 |
Transforming urban logistics requires innovative solutions and in this article we will feature three DISCO innovations that were developed and implemented within our Living Labs; Urban Access Control (UACs), Urban Freight Data Space (UDFS), and WareM&O.The integration of Urban Access Control (UAC) into transport systems has made route navigation smarter and more sustainable. In Ghent, UAC has been successfully implemented within the Dropon Transport Management System (TMS), offering real-time alternative routes to optimize logistics operations and reduce congestion.The Urban Freight Data Space (UFDS) facilitates secure, standardized data sharing among public and private stakeholders, enhancing last-mile deliveries. This platform is already helping cities improve urban logistics by enabling better collaboration and efficiency across various sectors.Additionally, WareM&O is a digital marketplace that connects warehouse owners with tenants, simplifying the process of leasing available space. This platform has been used in the DISCOESTATE pilot project in Thessaloniki, where underused buildings at TIF-HELEXPO were transformed into logistics hubs, improving freight efficiency and helping ACS Courier reduce congestion in the city.Together, these innovations are creating a more efficient, sustainable, and connected urban freight system, transforming logistics in cities worldwide.For more information, check the folder below for brief presentations on each innovation. |
|
|
Data spaces are a great way for cities to connect to logistics players in their cities, and integrate valuable city data directly into the logistics ecosystem. However, making city data available on the data space can come with some technical challenges, both in transforming the data and connecting to the data space. The Smart Data Platform reduces these obstacles to offering data on the data space by providing city data engineers with the tools they need to prepare their data for data space sharing and connect it to the data space. To achieve this, The Smart Data Platform makes use of a pre-existing data transformation (ETL) tool, packaged with a data space connector, which it connects through an overarching UI. This provides cities with all the capabilities of an ETL tool, while reducing the barrier to connecting to the data space. The below document serves as a setup guide for the Smart Data Platform and attached urban Freight data space connector. The setup guide follows the case study of the Ghent Living lab where data was gathered from the Gent Open Data Platform to the Smart Data Platform, and made available to the Disco network via the embedded Sovity dataspace connector (and UI). |
|---|
|
|
Data-level interoperability plays a vital role in a data space, and leveraging standard data models significantly simplifies this process. As a first proof-of-concept, this document shows how the DISCO project incorporates the APDS and DATEX II standards.APDS (Alliance for Parking Data Standards) is an international standard designed to establish a common language for sharing parking data. It aims to promote interoperability between parking systems and services, enabling seamless data exchange across various regions and platforms. DATEX II, on the other hand, is Europe's most widely adopted standard for road situations and traffic regulations. It provides a structured framework for sharing information related to traffic management, road conditions, and regulations, ensuring consistency and compatibility across European transportation systems.This document outlines mapping data from its sources to these two standards. It provides an overview of the APDS and DATEX II standards, detailing their structure and practical applications. Furthermore, it includes specific data mapping examples from the city of Ghent, demonstrating how real-world data can be transformed to comply with these standards. For an in-depth explanation of the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) technical implementation, including insights into the code and workflows used for this mapping within the framework of the Smart Data Platform, please refer to the DISCOLLECTION Design and Architecture Documentation |
|---|
 |
In Forum Virium Helsinki’s Future blog, our Smart City experts take a peek into the future of their fields, reflect on the change trends in Helsinki and present their vision of how science, technology and experience can best be used for the sustainable development of the city.Check it out here |
|---|
 |
Our latest best practice publication showcases pioneering measures implemented in the Helsinki Living Lab to make urban logistics more efficient and sustainable. The publication not only outlines the goals, implementation process, and key findings, but also offers practical insights and contacts for cities and organisations eager to take action.The report highlights four distinct approaches to monitoring and managing loading zones:
Together, these measures demonstrate how digital tools and innovative technologies can help cities reduce congestion, optimise urban space, and improve the coexistence of freight operations with other urban activities.This publication serves as a valuable resource for municipalities, planners, and logistics stakeholders seeking tested solutions to common challenges in urban freight and loading zone management. |
|---|
Learn from urban logistics insights, experience, and Living Labs demonstrations in Europe and beyond. Best practices and resource repository are valuable reference for individuals or organizations seeking to improve their knowledge on urban logistics. Here stakeholders can access proven approaches, tools, templates, case studies, and other resources to inform their decision-making and implementation efforts, ultimately fostering continuous improvement and innovation.
|
|
Data is a key source of competitive advantage, but only if shared securely and sovereignly. The IDS Reference Architecture Model (IDS-RAM) sets standards for trusted data sharing ecosystems, enabling smart products and innovative services. As the core of the International Data Spaces (IDS) concept, it defines key components, interactions, and governing principles for data space architectures. Developed collaboratively by companies, scientists, technologists, and policymakers, the IDS-RAM is the conceptual framework for designing and implementing data spaces.Link to the full IDS-RAM 4.0
Link to the IDS-RAM 4.0 repository |
|---|
 |
The Rulebook of the International Data Spaces Association (IDSA) provides functional, technical, operational, and legal requirements for building and operating data spaces based on the IDS-RAM , outlining mandatory and optional functionalities for various implementation approaches. It's designed for data space participants, data sharing initiatives, and anyone interested in data sharing standards or setting up data spaces, allowing them to assess alignment with the requirements IDSA suggests for trustworthy data spaces trustworthy data space . The Rulebook is accessible to readers with diverse backgrounds, not just lawyers or software engineers.Click on the IDSA Rulebook to learn more about the resourceFind the full IDSA Rulebook on GitBook |
|---|
 |
The Dataspace Protocol is a standardized set of rules developled and designed by the International Data Spaces Association (IDSA) to enable seamless and trusted data sharing within data spaces, similar to how HTTP works for web data. It promotes interoperability by defining schemas and protocols for key functions like data cataloging, contract negotiation, and usage agreements. By adhering to this protocol, organizations can align with industry standards, adopt best practices, and unlock new data-driven business models.Click on Dataspace Protocol to open the resource.Find a user-friendly version of the Dataspace Protocol on IDSA’s Knowledge Base |
|---|
 |
The open-source International Data Spaces (IDS) Reference Testbed reference testbed allows companies and organizations to develop and test data space components. The testbed helps them to build components that comply with the International Data Spaces (IDS) standard and then test them on their interoperability and prepare them for their IDS certification. This is crucial for enabling a data economy based on data sovereignty and trusted data sharing within data spaces, as the testbed facilitates the widespread adoption of necessary IDS components. |
|---|
 |
The Roadmap for Sustainable Urban Freight in ASEAN provides a strategic framework designed to help ASEAN cities transition toward more sustainable, resilient, and efficient urban freight systems. The roadmap is structured into three key phases—short, medium, and long-term—allowing cities to implement actions progressively based on their specific capacities, challenges, and goals. The methodology behind the roadmap involves a phased approach, ensuring that cities can build a solid foundation before moving toward more complex interventions. The actions proposed in the roadmap are based on a thorough analysis of regional challenges and opportunities, incorporating insights from research, stakeholder engagement, and private sector input.This strategic roadmap provides a clear direction for ASEAN cities to address their urban freight challenges while promoting sustainable development aligned with broader regional and global goals. By addressing the specific challenges and leveraging the opportunities inherent in the ASEAN context, these guidelines pave the way for sustainable changes in urban freight and logistics management across the region.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
BOOSTLOG Vision is transforming European freight transport and logistics R&I ecosystem to perform optimally boosting impact generation out of R&I investment contributing to |
|---|
Shenzhen, recognized as the inaugural city worldwide to implement zero-emission freight zones in 2018, established 10 "green logistic zones." These zones permit all-day access for electric freight vehicles under 4.5 tonnes while banning fossil fuel freight vehicles entirely. By the end of 2019, Shenzhen boasted over 70,000 battery-electric freight vehicles in operation, surpassing the number of electric buses and taxis, marking the city as home to the largest operational electric fleet. |
|---|
Confluence, spanning 1.5 km² in Lyon, aims to create a tranquil, low-motorized environment while enhancing public space utilization. The district's massive urban construction challenges traditional automotive mobility and logistics flows. |
|---|
 |
Logistics professionals have faced increased demand and challenges but have maintained the supply, earning appreciation for their dedication. Despite progress, there's still a significant distance to cover in achieving green freight objectives, emphasizing the need for prompt action. The overarching goal of the Transport Decarbonisation Alliance is to foster global cooperation towards greener transport, with this guide serving to support partners by sharing experiences and promoting the potential of zero-emission freight. Through this guide "Don’t wait to start with freight" the intention is to extend support to these partners by sharing the experiences of ZEZ-F pioneers and highlighting the vast potential of zero-emission freight.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
As the fight against climate change intensifies, Urban Vehicle Access Regulations (UVARs) are gaining popularity for their potential to reduce emissions and enhance air quality. UVARs encompass measures such as Low Emission Zones, Traffic Limited Zones, Pedestrianisations, and Parking Regulations. However, their implementation often faces challenges due to their broad impact beyond geographical boundaries, affecting factors like accessibility, social inclusion, and affordability. While the UVAR SUMP Topic guide published in 2019 provides valuable insights, further guidance is needed, especially regarding stakeholder engagement, complementing measures, and information for tourists. Projects like Dynaxibility4CE produced additional guidance documents and tools, including an annex elaborating on UVAR implementation considering Functional Urban Areas (FUAs).Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
Across Europe, local authorities are addressing this air and noise pollution, congestion and safety issues by implementing Urban Vehicle Access Regulations (UVARs), which prioritize sustainable mobility and restrict vehicle access in urban areas, particularly private cars, to create more livable cities focused on people rather than cars. UVARs encompass measures like Low Emission Zones, congestion charges, Limited Traffic Zones, and alterations to road layouts. Accordingly, this document presents the insights of the six cities (Bielefeld, Helmond, Jerusalem, City of London, Padova and Vitoria-Gasteiz) integrated UVARs into their standard urban mobility strategies within The Horizon 2020 project ReVeAL (2019-2022) context.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
Recent years have witnessed rapid growth in ride-hailing and ride-sharing, advancements in powertrain technologies, and the deployment of connected cars, with the imminent arrival of autonomous vehicles. The integration of multi-modal trip planning is becoming increasingly feasible, reflecting consumer preferences for convenient and sustainable mobility options. To facilitate this change effectively, a shared digital framework is necessary to aggregate data from various sources, offering real-time insights into the urban environment and this report adopts a comprehensive perspective, examining how the principles of mobility data sharing can address the constraints faced by various stakeholders such as governments, businesses, and citizens.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
Through a combination of innovative technology solutions, collaborative schemes driven by the sharing economy, and policy interventions, ULaaDS seeks to catalyze systemic changes in urban and peri-urban service infrastructure, aligning with sustainable urban mobility plans (SUMPs). ULaaDS endeavours to accelerate the deployment of shared and zero-emission solutions to meet the challenges posed by the growing on-demand economy in urban logistics. Followingly, this document emphasizes the factors that drive adoption, barriers to implementation, and essential components for successful pilot and trial implementations in the context of Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans (SUMP) or Sustainable Urban Logistics Plans (SULP) development.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
ULaaDS (Urban Logistics as an on-Demand Service) aims to revolutionize urban logistics by fostering sustainable and livable cities through the re-localization of logistics activities and the restructuring of freight flows. Through a blend of innovative technology solutions, collaborative sharing economy initiatives, and policy interventions, this ULaaDS policy paper aims is to underscore practical insights from trials, including the optimization of urban space allocation, engagement of stakeholders for success, promotion of fair competition in freight transport, and understanding the technological solutions. These insights were collaboratively compiled by ULaaDS partners representing seven ULaaDS cities.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
The Alliance for Logistic Innovation and Collaboration in Europe (ALICE) has developed the "Towards Zero Emissions Logistics 2050" roadmap to provide practical guidance for companies and stakeholders in achieving decarbonization goals. The roadmap emphasizes the need for collaboration and efficiency gains in freight transport and logistics, focusing on leveraging existing assets, integrating flows, and maximizing capacity utilization. The document offers an overview of existing roadmaps, a framework for decarbonization, and specific actions for stakeholders to undertake individually or collectively to facilitate the transition towards sustainable freight management.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
This paper provides insights for urban planners regarding cargo e-bikes, outlining successful deployments in North America as replacements for ICE vehicles and proposing strategies to promote their adoption while ensuring safety for all road users. Drawing from data and opinions of key stakeholders in the public and private sectors, and leveraging the expertise of the Urban Freight Lab, the paper offers nine recommendations and 21 actionable strategies across four thematic areas: culture and education, infrastructure, policy and regulation, and incentives. covering topics including labour force training, cycling infrastructure, e-bike laws, and purchase incentives.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
Parcel lockers have rapidly emerged as a popular innovation in cities, outpacing the development of associated policies and regulations, prompting public authorities to seek ways to manage their proliferation while mitigating potential impacts on public spaces and traffic. The City of Groningen, in collaboration with the University of Groningen and Bax & Company have developed a framework for an open parcel locker system, involving interdepartmental collaboration, stakeholder engagement, academic studies, benchmarking of international practices, and spatial analysis for optimal placement. In this paper, the focus is on ten specific locations identified for their significant potential to improve accessibility in densely populated areas of the city.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
Aligning with the framework outlined in the European Commission's Urban Mobility Package and the European SUMP Guidelines (second edition), the Sustainable Urban Logistics Planning (SULP) guide aims to furnish authorities with a structured approach to implementing actions within the SUMP context, effectively addressing challenges and achieving sustainable urban logistics policy and planning. By integrating best practices of tools, methods, and techniques applicable across various stages of the revised SUMP process, along with measures and interventions, the guide aims to provide practical assistance to readers in realizing the future sustainability objectives of their cities.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
This collaborative guide represents a joint effort between POLIS, the network of European cities and regions dedicated to transport innovation, and ALICE. Its purpose is to consolidate the perspectives of various stakeholders and experts, offering guidance to local and regional authorities, national and EU governments, companies, civil society, and citizens. By providing a framework for organizations to align their agendas with the objectives outlined in the document, it calls for collective action and collaboration, recognizing that no single stakeholder can effectively address the challenges alone. The guide seeks to unite diverse stakeholders and experts to contribute to the advancement of sustainable and livable urban environments.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
The evolution of logistics real estate tailored to professionals and considerate of urban requirements has emerged as a viable solution, facilitating mobility optimization and hastening the decarbonization of distribution operations. This handbook exemplifies the ongoing tension between various scales, functionalities, and divergent perspectives among stakeholders. The key challenge lies in reframing the perspective: does real estate cater to the logistics needs of the city, or do logistics operators shape their operations based on available real estate? To what extent can urban logistics be planned or guided to serve the interests of territories and their inhabitants? This guide reflects the dynamic interplay between urban development and logistical demands.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
The Novelog Toolkit is a user-friendly tool designed to assist users in identifying city logistics measures and their impacts based on selected parameters. Users can choose relevant parameters and press "search" to view a list of measures and impacts implemented in cities with similar parameters. The toolkit allows users to explore the impacts of specific measures by selecting them and pressing the "search" button. Information regarding the implementation location, timing, and impacts of the chosen measure is provided. Users can further refine their search by selecting specific city parameters.Link to Tool kit |
|---|
 |
This report provides targeted advice to policy makers on proactive measures to manage the complexities of urban logistics and facilitate the uptake and success of urban logistics hubs. The report expands on the expert discussions during the International Transport Forum (ITF) Roundtable, “Urban Logistics Hubs”, held in Paris and by video conference on 26–27 June 2023. Laetitia Dablanc (Université Gustave Eiffel, Paris) chaired the Roundtable discussions.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
On February 18, 2025, the final event of the PILL and SYTADEL projects in Brussels showcased advancements in the Physical Internet (PI) and synchromodal logistics. PILL developed a PI blueprint and software stack, while SYTADEL focused on creating a Flemish logistics data space for synchromodal transport. Key takeaways included discussions on Flemish logistics innovation, technical advancements, industry perspectives on synchromodality, and ALICE's contributions. ALICE highlighted the alignment of PI with zero-emission logistics goals and the need for collaboration, standardization, and asset sharing. Breakout sessions explored technical and business aspects, emphasizing the importance of industry collaboration, governance, and scalable solutions for wider adoption. The event highlighted that synchromodal transport and PI are moving from theory to reality, requiring continued collaborative effort.Link to the website |
|---|
 |
This discussion paper by ALICE addresses inefficiencies in logistics stemming from fragmented data, paper processes, and system silos, proposing a new level of data synchronization. It argues against relying solely on disparate government or monolithic industry platforms and instead advocates for a peer-to-peer data sharing model where owners retain control. The core proposal involves two components: a common high-level language (ontology) to provide a universal semantic layer for logistics operations, leveraging existing standards, and the adoption of modern, secure communication protocols (based on W3C standards) for real-time data exchange. A proof-of-concept by GEODIS demonstrated the feasibility of this approach for synchronizing processes across partners. The paper concludes by urging logisticians to actively engage in defining these open standards to avoid future fragmentation and ensure interoperability, suggesting the creation of a dedicated Logistics Data Space.Link to the pdf |
|---|
The European Union is implementing the Electronic Freight Transport Information (eFTI) Regulation to digitalize freight transport across all modes, aiming for a fully paperless system by July 2027. This initiative is projected to yield significant benefits, including reduced administrative burdens, enhanced data security, improved logistical efficiency, and substantial cost savings for the transport and logistics sector, while also contributing to sustainability goals. Key challenges for successful implementation include IT system development, ensuring cybersecurity, and securing widespread adoption, particularly among SMEs, necessitating strong collaboration between stakeholders and proper resourcingLink to the website |
|---|
 |
The ongoing 2023-2026 GRETA project is tackling the challenge of greening last-mile freight in seven Central European cities – Bologna, Helsinki, Lyon, Maribor, Poznan, and Reggio Emilia. They're testing cool ideas like zero-emission vehicles, local microhubs, and smarter street management. While Bologna, Helsinki, and Lyon are already rolling out their plans (think microhubs and a central hub in Lyon), Maribor, Poznan, and Reggio Emilia are still in the planning stages, likely focusing on microhubs too. To learn from others and share ideas, GRETA has also set up a regular meeting group with similar projects, with workshops happening roughly every three months to dive deep into specific urban logistics topics. Ultimately, GRETA's work promises to make a real difference in creating more sustainable city deliveriesLink to the website |
|---|
 |
The European Commission's Expert Group on Urban Mobility (EGUM) recommends several key actions for Sustainable Urban Logistics Plans (SULPs), including establishing an EU-wide approach for data collection and sharing, updating SULP guidelines to incorporate new elements and innovations, providing expert support to local authorities, setting national policies for worker safety and collaborative logistics, strengthening public-private partnerships, and encouraging sustainable e-commerce practices, all aimed at optimizing urban goods transportation for environmental and efficiency benefits.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
This document, "Recommendations on Urban Logistics - Mobility and Transport," by the European Commission's Expert Group for Urban Mobility, focuses on the critical role of data sharing in optimizing urban logistics. It highlights the challenges and mutual benefits for both public and private sectors in sharing data to improve decision-making, performance measurement, and long-term urban planning. The recommendations emphasize voluntary data sharing and the use of simple IT tools by cities to collect and share data, ultimately aiming for more sustainable and efficient urban freight transport through better data access and digitalization of relevant regulations and assets.Link to the pdf |
|---|
 |
The document "EGUM Recommendations SG4 D3 InnovationUptake" offers guidelines on enhancing urban logistics through innovation to decrease emissions amid rising demand, providing specific recommendations for local authorities to use regulations and incentives, establish testing environments, engage in research, and optimize urban planning; for private stakeholders to embrace innovation through participation, feedback, sustainable practices, and infrastructure support; and for member states to utilize funds, revise laws, offer guidance, and support the deployment of clean vehicles and micro-hubsLink to the pdf |
|---|
|
|
This deliverable presents the analysis conducted to define the technical infrastructure requirements necessary for the deployEMDS project. Leveraging frameworks from the Open Data Product Specification (ODPS) and the Data Space Business Alliance (DSBA) Technical Convergence document, a bottom-up approach was adopted to address the diverse requirements of the nine implementation sites. This methodology emphasised a capability-driven design to establish a scalable, secure, and flexible data space, ready to meet the evolving needs of the European mobility sector. Through an intake and mapping process, the essential technical, functional, and operational capabilities required by the data space to support use cases at various implementation sites were identified. This included specifying components such as data governance mechanisms, authentication, authorisation, and accounting protocols, along with interoperability standards crucial for the efficient management and exchange of mobility data. Additionally, requirements stemming from best practices and state of the art were added to reach the minimum viable capabilities for the data space. This process did not result in requirements for a specific data space standard, indicating that the methodology and results are implementation-agnostic. This supports a later decision that should be based on a hands-on feasibility study.For more information, click here to access the Full Report. |
|---|
|
|
This technical report presents the outcomes of Task 2.2 of the deployEMDS project, which focuses on specifying the data space architecture and building blocks in line with the European Data Spaces technical framework. As part of Work Package 2, "Deployment of an operational data space across borders", this task builds on the project’s use case requirements and defines the business processes needed for a functional data space to be deployed. To support the selection of the most suitable technical foundation for the deployEMDS architecture, the project team developed a comprehensive methodology. This approach involved translating use case requirements into customer journeys and related business processes, mapping them to essential data space building blocks, and evaluating existing software stacks. The work is conceptually grounded in the Data Space Blueprint developed by the DSSC, which outlines key organisational and technical building blocks for data spaces. Three software stacks were analysed:• Eclipse Data Space Components (EDC) – a mature, industry-driven open-source initiative offering a reference implementation of a data space connector and the underlying Data Space Protocol• FIWARE Data Space Connector – an implementation developed by the FIWARE Foundation to connect FIWARE-based technologies to data spaces• Simpl – a European Commission-driven open-source initiative to support the implementation of Common European Data SpacesFor more Information, click here to access the full report |
|---|
|
|
Urban logistics plays a critical role in sustaining the economic and social life of European cities, yet it remains one of the most complex and least efficient areas of transport. To support the transition towards cleaner, smarter, and more sustainable mobility, the European Commission launched a targeted survey on urban logistics across 21 major European urban areas. This study represents the first comprehensive and systematic effort to collect harmonised data on freight deliveries in cities, examining fleet composition, business models, vehicle technologies, and operational practices.The results provide valuable insights into current urban freight patterns, highlight challenges such as emissions, congestion, and data fragmentation, and identify opportunities for collaboration, innovation, and low-emission logistics solutions. Serving as a baseline for future research, the study offers practical evidence to guide city authorities, planners, and policymakers in developing Sustainable Urban Logistics Plans (SULPs) and in advancing the objectives of the European Green Deal and the Sustainable and Smart Mobility Strategy.The report is available in English and French, and you can access it from here |
|---|
|
|
Urban freight is at the heart of Europe’s decarbonization challenge, with growing demand for efficient delivery services often clashing with sustainability goals. This presentation explores the new setting and prospects of the urban freight market, highlighting how ALICE contributes to shaping solutions that reduce emissions, foster collaboration among stakeholders, and support European cities in their transition toward cleaner, more resilient logistics systems.For more Information, you can click here |
|---|
|
|
Urban logistics is increasingly challenged by e-commerce growth, congested streets, and conflicting demands for curb space. This presentation explores how curbside management can be transformed through data-driven, collaborative governance to support more efficient, equitable, and decarbonized urban freight operations. It highlights how shared digital platforms, flexible curb allocations, and integrated stakeholder frameworks align with the Physical Internet paradigm, offering new pathways for European cities to meet sustainability goals while better serving businesses, citizens, and logistics providers.For more Information, you can click here |
|---|
Explore funding opportunities in this section, featuring calls for proposals, tenders, and financing guidelines tailored for Living Labs and cities who wish to plan, develop and implement urban logistic measures. Discover funding guidance and access valuable resources to support the financial aspects of your Living Lab initiatives.
🔔 Main Innovation Open Call 2025 by EIT Urban Mobility launched!
8M EUR is available to support innovative projects in two high-impact strategic sectors: urban logistics and energy transition.
Key dates of the Call calendar:
– Call opening: 4 April 2024
– Call closure: 4 June 2024 at 17:00 CET
– Eligibility and admissibility check: June 2024
– External evaluation of proposals (1st stage): June-July 2024
– Invitations to hearings (2nd Stage): July 2024
– Hearings: September 2024
– Communication of results: October 2024
– Tentative start of the projects: November/December 2024
More information here !
 |
The 2025 European Innovation Council (EIC) Accelerator Challenges, with a €250 million budget (€50 million per challenge), will support SMEs in five key areas: advanced materials (scaling critical technologies for strategic autonomy), low-emission food production (reducing agricultural greenhouse gas emissions via biotechnology), generative AI (developing transformative AI solutions), space infrastructure (innovative in-space servicing and asset protection), and future mobility (reducing transport emissions). These challenges aim to foster European innovation, sustainability, and competitiveness.Link to the website |
|---|
 |
The European Space Agency (ESA) is seeking innovative businesses to leverage space technologies for groundbreaking applications. The ESA BASS program offers funding opportunities for companies of all sizes to develop and validate cutting-edge solutions in various sectors, including transport, logistics, and more. This presentation will delve into the strategic objectives and funding opportunities of ESA's open calls for proposals, highlighting success stories from previous beneficiaries. Join us to learn about the application process, eligibility criteria, and how to tap into the potential of space technology to drive innovation and business growth.Link to the website |
|---|
Dive into the training activities we prepare for you. Stay updated on upcoming news about our learning opportunities, and access our training materials to engage with the content at your convenience. This section offers a comprehensive view of our diverse training initiatives, spanning webinars, e-courses and podcasts, providing practical insights and tools to address urban logistic opportunities and challenges head-on. Engage with our training activities in our dynamic forums feature to share insights, connect with professionals, and contribute to collaborative innovative urban logistics solutions.
Find our e-courses and webinars on: 
 |
This webinar focused on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for urban logistics, explaining their importance and application in measuring solutions and initiatives. Targeted at policymakers and city representatives, the session highlighted the DISCO project's approach to KPI selection, emphasizing alignment with strategic goals and practical implementation. The webinar covered KPI measurement methods, sustainability considerations, showcased the DISCO KPI dashboard, and featured the Thessaloniki Living Lab's experience in defining KPIs, including challenges and lessons learned..Link to the website |
|---|
 |
This webinar explores Data Spaces, focusing on their role in enabling secure, interoperable data sharing. It will cover the core principles, benefits, and architecture of Data Spaces before transitioning to a practical demonstration of the DISCO Urban Freight Data Space. Participants will see how datasets are shared via a user-friendly interface and visualized using a geo-JSON application. Targeted at urban planners, logistics professionals, smart city developers, IT specialists, and data engineers, the session will conclude with a discussion of future development plans for the DISCO Data Space.Link to the website |
|---|
 |
Global e-learning programme on electric mobility Zero-Emission urban freightThe fifth course of the SOLUTIONS plus Global Learning Programme on electric mobility focuses on the connection between e-mobility and urban freight decarbonization. It explores challenges, trends, and strategies for making last-mile logistics more sustainable, featuring real-world examples from various cities. The course is designed for city and regional authorities but is also open to the public and benefits from the expertise of multiple organizations.Link to the website |
|---|
 |
Unlocking the potential of Digital Twins for sustainable on-demand urban logistics
|
|---|
 |
The ALICE webinar on January 29, 2025, focused on parcel lockers for urban last-mile delivery, stressing city-business collaboration. Key presentations included the NYC pilot (Solecki), Valence's out-of-home delivery expansion, and the CRP's plan (Vollmer) for 24/7 London lockers to ease traffic and improve air quality. The CRP is targeting transport hubs and community centers for efficient implementation. The webinar concluded with a roundtable on the pros, cons, and implementation of parcel lockers.Link to the webinar |
|---|
 |
The webinar on March 6th, 2024, as part of the POLIS – ALICE Greening Urban Freight Webinar Series 2024 #1, focused on the Physical Internet (PI) concept for more efficient and sustainable urban logistics, emphasizing resource pooling, real-time data sharing, and route optimization within open, connected networks; the event showcased the EU-funded URBANE and DISCO projects promoting sustainable last-mile transport and data-driven logistics through presentations on living labs in Bologna and urban access control, with a shared vision between POLIS and ALICE to accelerate the transition to greener urban freight..Link to the website |
|---|
 |
The webinar, a joint effort by ALICE and EUROCITIES, focused on the crucial topic of finding space for mobility and logistics data within the context of EU policies and technological advancements. It explored current practices in the European mobility data space and its application in the logistics sector. The event brought together experts and pioneers to discuss technical developments and implementation, aiming to foster collaboration among stakeholders like urban mobility and logistics practitioners, policymakers, and researchers to achieve zero-emission urban logistics. Key projects like DISCO and deployEMDS, which are actively working on the European Mobility Data Space, were also highlighted during the webinar.Link to the website |
|---|
 |
This course brings together knowledge, experience, and lessons learned from the DISCO Starring Living Labs, offering practical tools and methodologies to assess urban logistics solutions through the Mastering Evaluation for Sustainable Urban Logistics Solutions process. It also explores how to link these evaluation techniques to local, national, regional, and international policy frameworks such as Sustainable Urban Logistics Plans (SULPs) and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The course equips you with the essential skills to apply these evaluation methods to drive smarter, more sustainable urban logistics solutions.Link to the website |
|---|
Join the Conversation and Make Your Voice Heard! Our Citizen Participation and Engagement Section empowers users to actively engage in discussions, share feedback, and contribute ideas. Together, we shape the future of our community through inclusive participation and meaningful engagement.